53%
MIGRAINE DAY REDUCTION WITH QULIPTA 60 mg (n=216)2
-1.03 WMD from 1.93 baseline
VS
15%
MIGRAINE DAY REDUCTION WITH PLACEBO (n=211)2
-0.29 WMD from 1.88 baseline
Real QULIPTA patient.

Primary endpoint: Mean MMD reduction across 12 weeks
MMD reduction across 12 weeks with QULIPTA® 60 mg (4.2 fewer MMD from 7.8 baseline) (n=222; P<0.001) vs 33% with placebo (2.5 fewer MMD from 7.5 baseline) (n=214)1
MMD=Monthly Migraine Days.
Response rates
Secondary endpoint: Percentage of patients who achieved ≥50% MMD reduction across 12 weeks1
WEEKS 1-12 61% (n=222; P<0.001) vs 29% with placebo (n=214)1
Similar 12-week average results were seen with other doses1:
Additional endpoint: Percentage of patients who achieved ≥50% MMD reduction in Weeks 1-4, 5-8, and 9-124
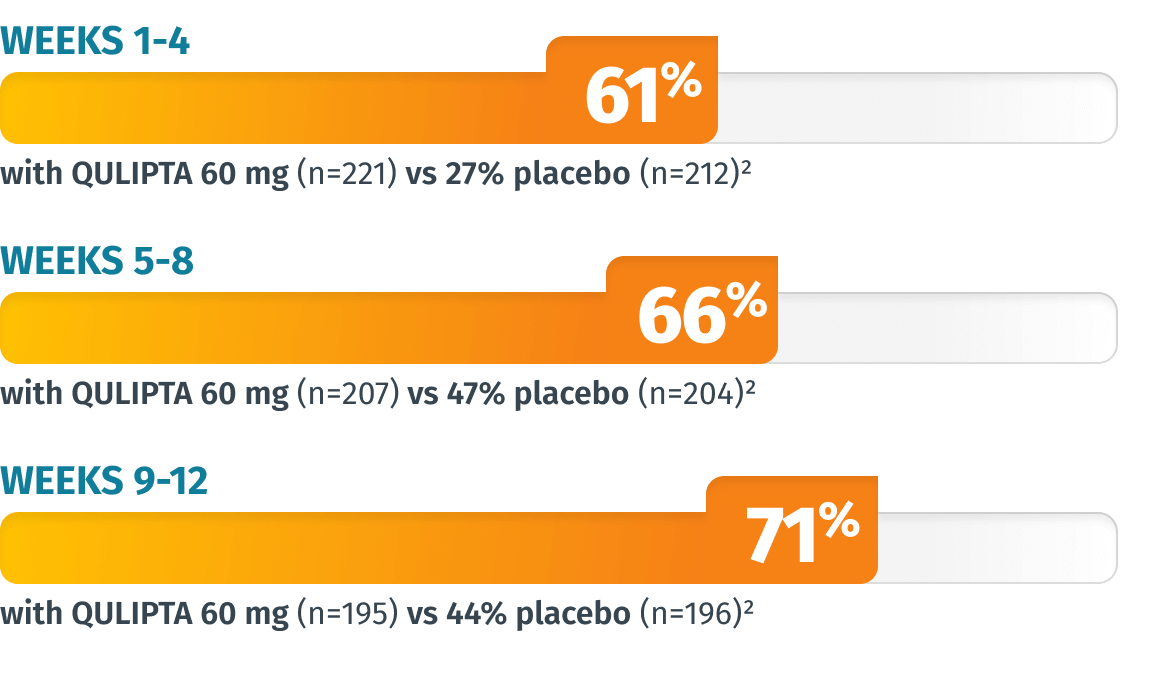
LIMITATIONS: The additional endpoints were prespecified, non-ranked endpoints and were not adjusted for multiplicity. Therefore, treatment differences cannot be regarded as statistically significant.
Additional endpoint: Percentage of patients who achieved 100% MMD reduction across 12 weeks4
WEEKS 1-12 8% (n=222) vs 1% with placebo (n=214)2
Similar 12-week average results were seen with other doses2:
Additional endpoint: Percentage of patients who achieved 100% MMD reduction in Weeks 1-4, 5-8, and 9-124
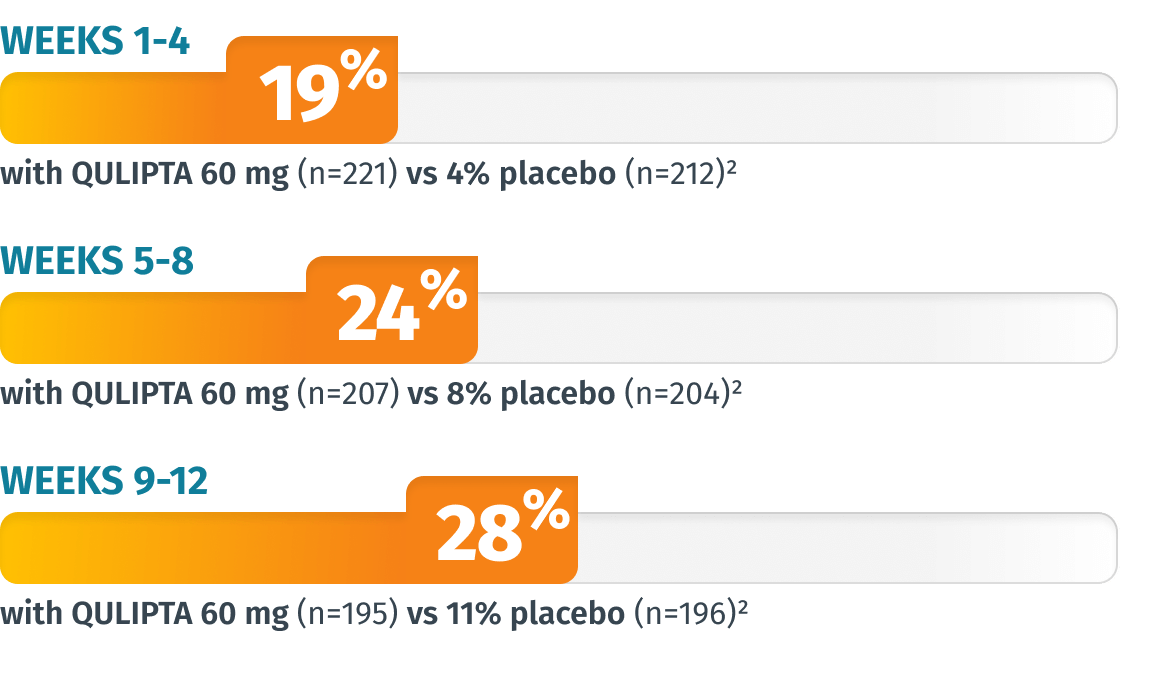
LIMITATIONS: The additional endpoints were prespecified, non-ranked endpoints and were not adjusted for multiplicity. Therefore, treatment differences cannot be regarded as statistically significant.
Additional endpoint: Change from baseline in weekly migraine days (WMD) at Week 1
53%
MIGRAINE DAY REDUCTION WITH QULIPTA 60 mg (n=216)2
-1.03 WMD from 1.93 baseline
VS
15%
MIGRAINE DAY REDUCTION WITH PLACEBO (n=211)2
-0.29 WMD from 1.88 baseline
LIMITATIONS: The additional endpoints were prespecified, non-ranked endpoints and were not adjusted for multiplicity. Therefore, treatment differences cannot be regarded as statistically significant.
Secondary endpoint: Change from baseline in mean monthly AIM-D PDA scores across 12 weeks
*The 10 mg results were not statistically significant.1
Post-hoc analysis: Change from baseline in performance of daily activities at Week 1 as measured by AIM-D PDA
LIMITATIONS: Performance of daily activities at Week 1 as measured by AIM-D PDA was a post-hoc analysis that was not prespecified or adjusted for multiplicity. Therefore, treatment differences cannot be regarded as statistically significant.
AIM-D PDA=Activity Impairment in Migraine-Diary Performance of Daily Activities.
HIGH FREQUENCY
~19 MMD1
PREVENTIVE TREATMENT EXPERIENCE
83% had preventive exposure2
SEVERE DEBILITATION
>15 acute medication use days;
~43 MSQ-RFR score1
MEDICATION OVERUSE
Nearly two-thirds of patients who were studied overused acute medication2

Primary endpoint: Mean MMD reduction across 12 weeks1
Migraine Day Reductions
QULIPTA 60 mg: -6.9 days from 19.2 baseline MMD
(n=256) (P<0.001)1
Placebo: -5.1 days from 18.9 baseline MMD
(n=246)1
INDICATION
QULIPTA® (atogepant) is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
QULIPTA is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to atogepant or any of the components of QULIPTA.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Cases, including anaphylaxis, dyspnea, rash, pruritus, urticaria, and facial edema, have been reported with use of QULIPTA. Hypersensitivity reactions can occur days after administration. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue QULIPTA and institute appropriate therapy.
Hypertension (HTN): Development or worsening of pre-existing HTN has been reported following the use of CGRP antagonists, including QULIPTA. Some patients who developed new-onset HTN had risk factors. There were cases requiring initiation of HTN treatment and, in some cases, hospitalization. HTN may occur at any time but was most frequently reported within 7 days of initiation. QULIPTA was discontinued in many of the cases. Monitor patients for new-onset or worsening of pre-existing HTN, and consider whether discontinuation of QULIPTA is warranted if evaluation fails to establish an alternative etiology or blood pressure is inadequately controlled.
Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP): Development, recurrence, or worsening of pre-existing RP has been reported following the use of CGRP antagonists, including QULIPTA. In cases with small molecule CGRP antagonists, symptom onset occurred a median of 1.5 days following dosing. Many of the cases reported serious outcomes, including hospitalizations and disability, generally related to debilitating pain. In most cases, discontinuation of the CGRP antagonist resulted in resolution of symptoms. QULIPTA should be discontinued if signs or symptoms of RP develop, and patients should be evaluated by a healthcare provider if symptoms do not resolve. Patients with a history of RP should be monitored for, and informed about the possibility of, worsening or recurrence of signs and symptoms.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (at least 4% and greater than placebo) are nausea, constipation, and fatigue/somnolence.
Dosage form and strengths: QULIPTA is available in 10 mg, 30 mg, and 60 mg tablets.
US-QLP-250104
Please see full Prescribing Information.